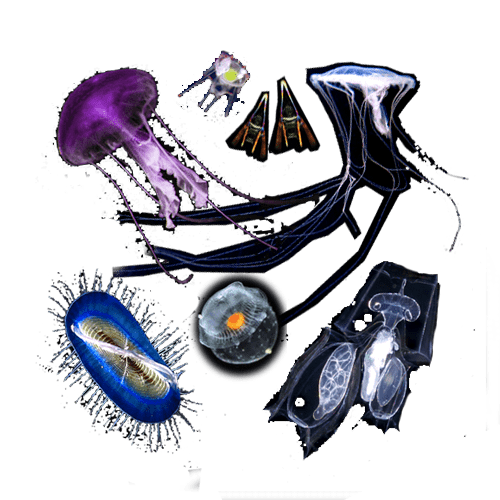
In this episode
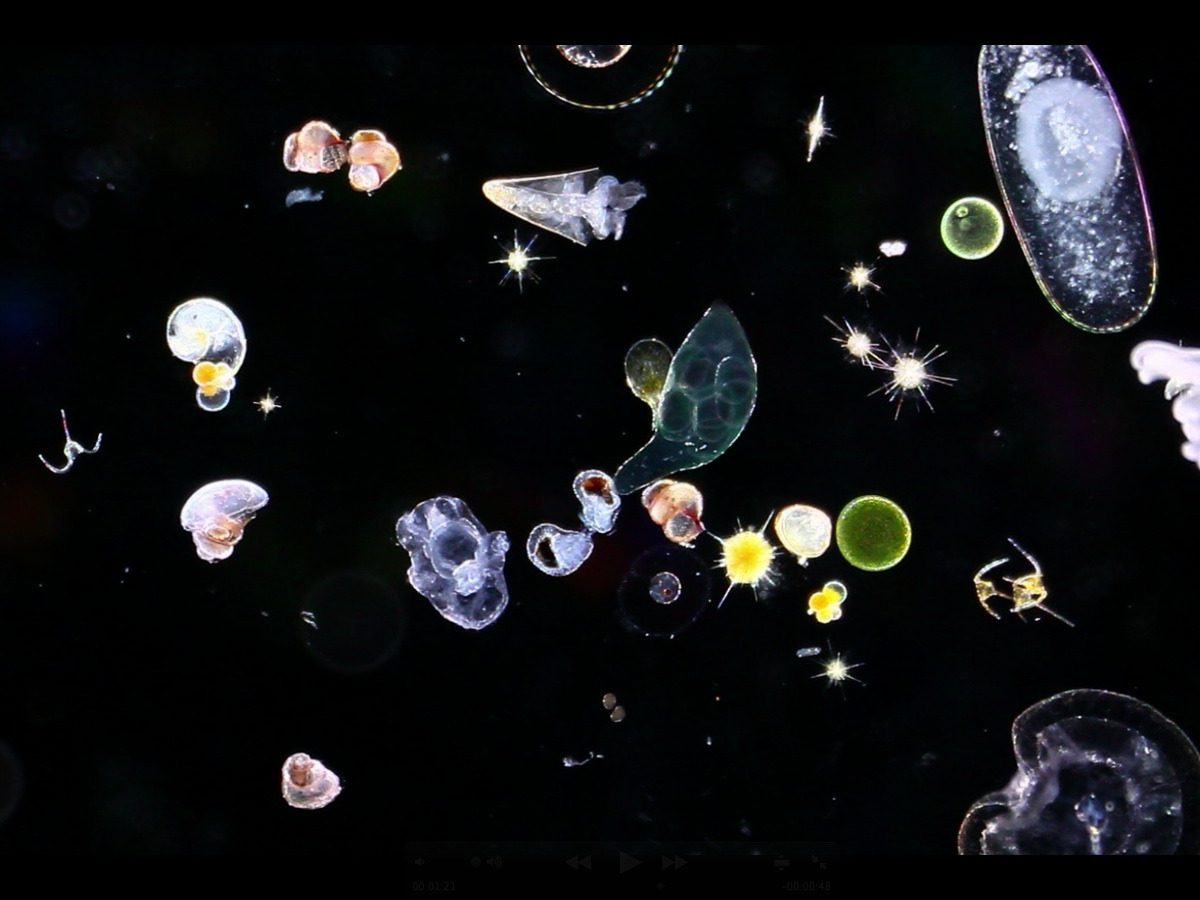
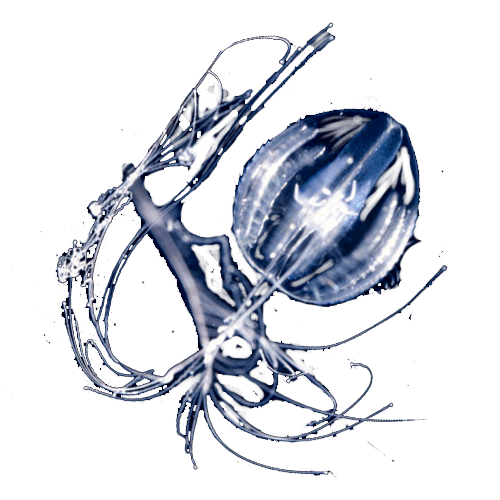
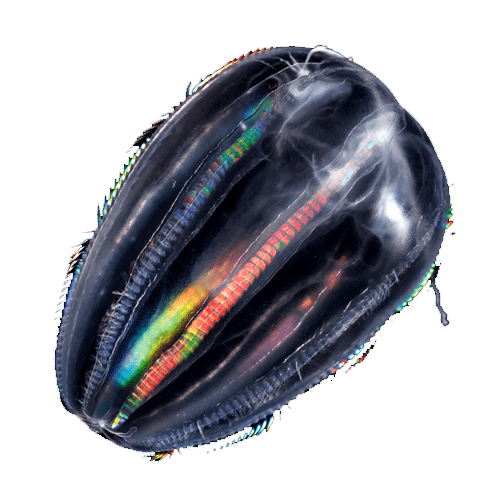
 Siphonophores
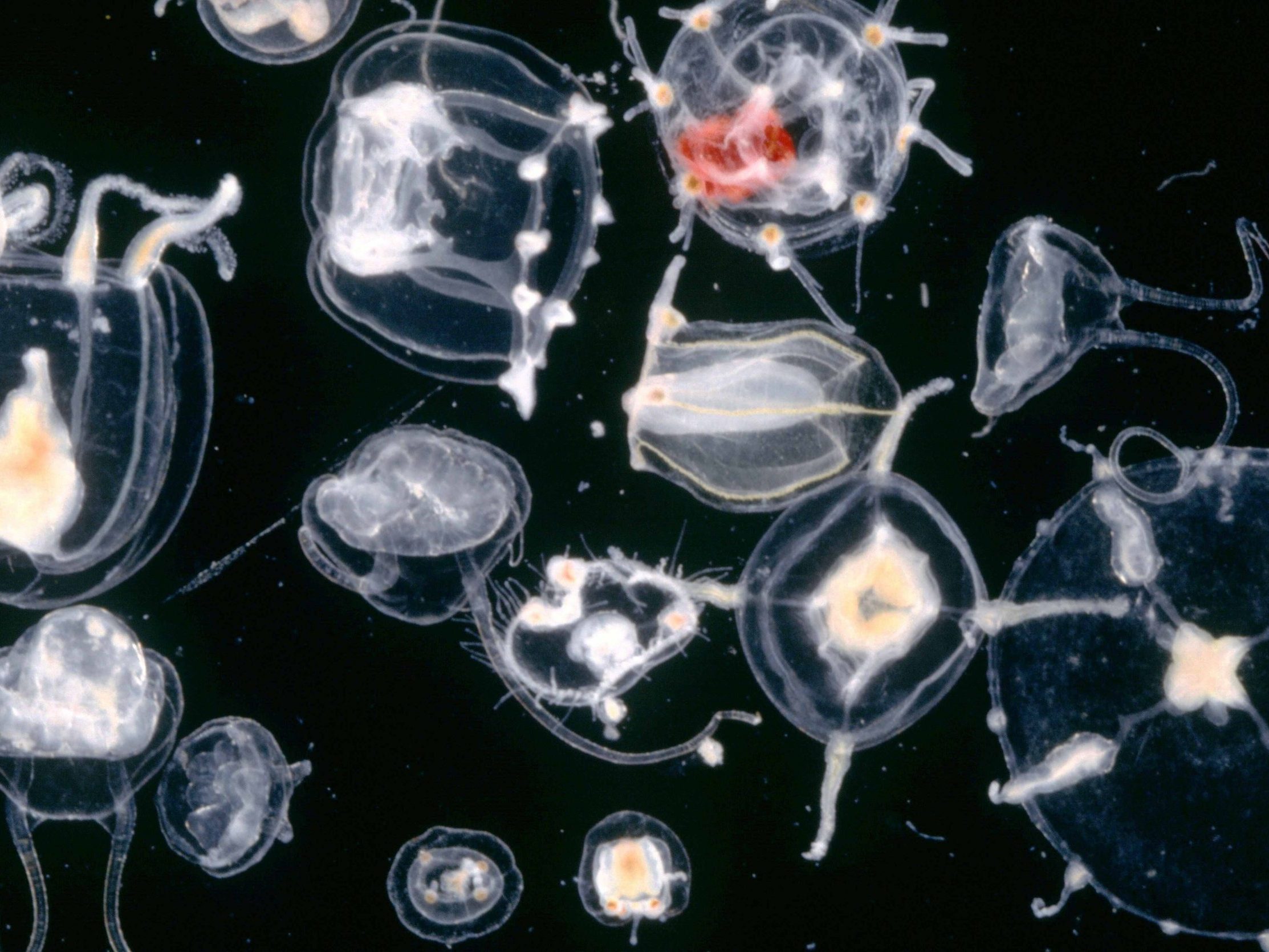
Siphonophores ClytiaClytia hemispherica
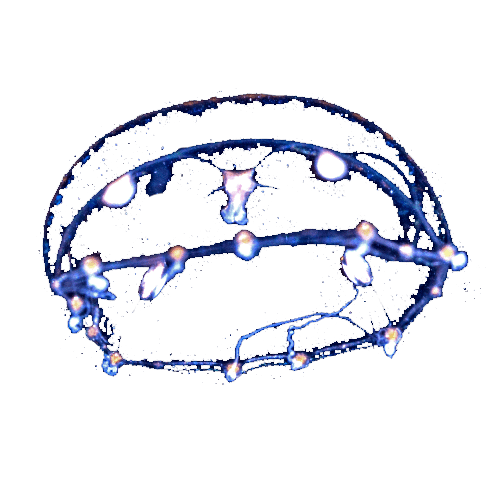
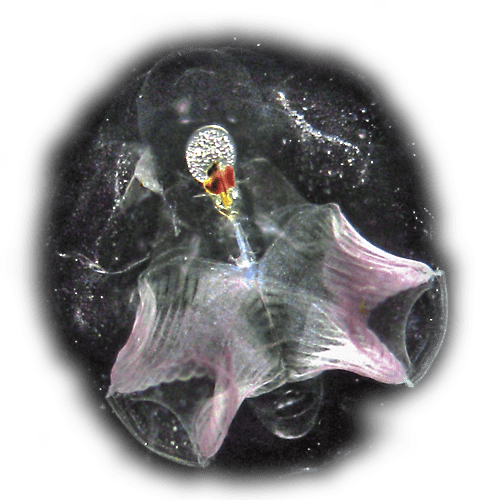
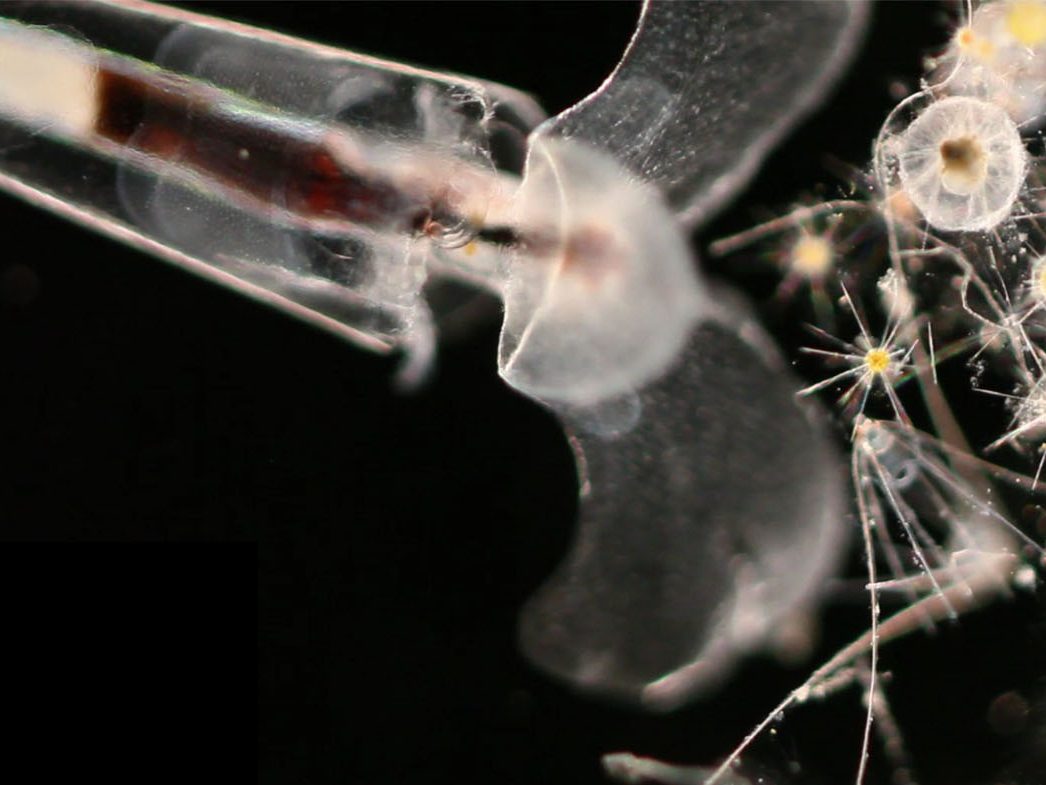
ClytiaClytia hemispherica Velella larvaVelella velella
Velella larvaVelella velella Anthozoan larva
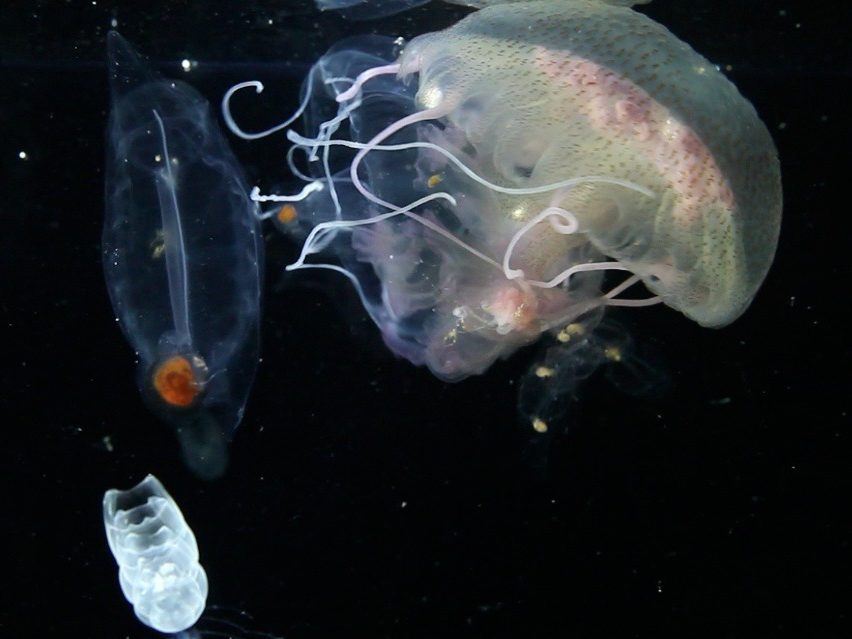
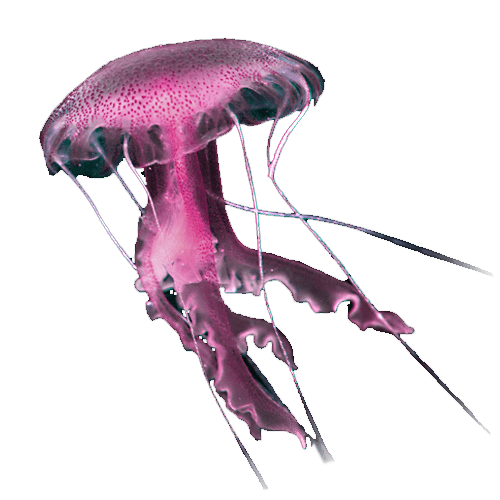
Anthozoan larva PelagiaPelagia noctiluca
PelagiaPelagia noctiluca
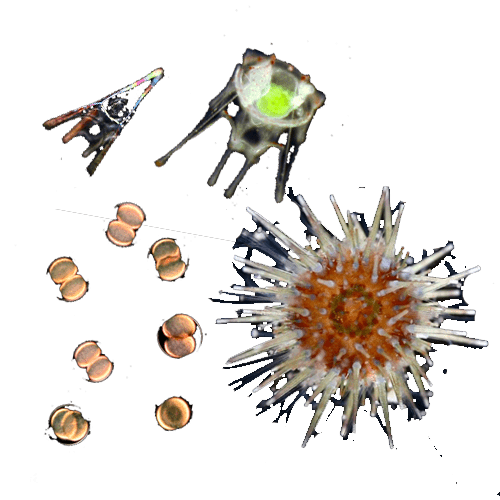
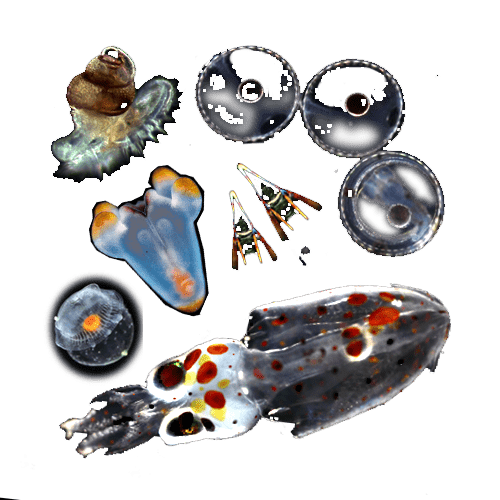
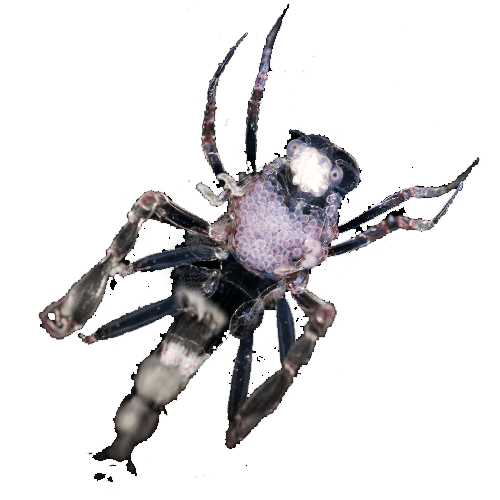
 Phronima
Phronima
 Beroe engBeroe ovata
Beroe engBeroe ovata LeucotheaLeucothea multicornis
LeucotheaLeucothea multicornis
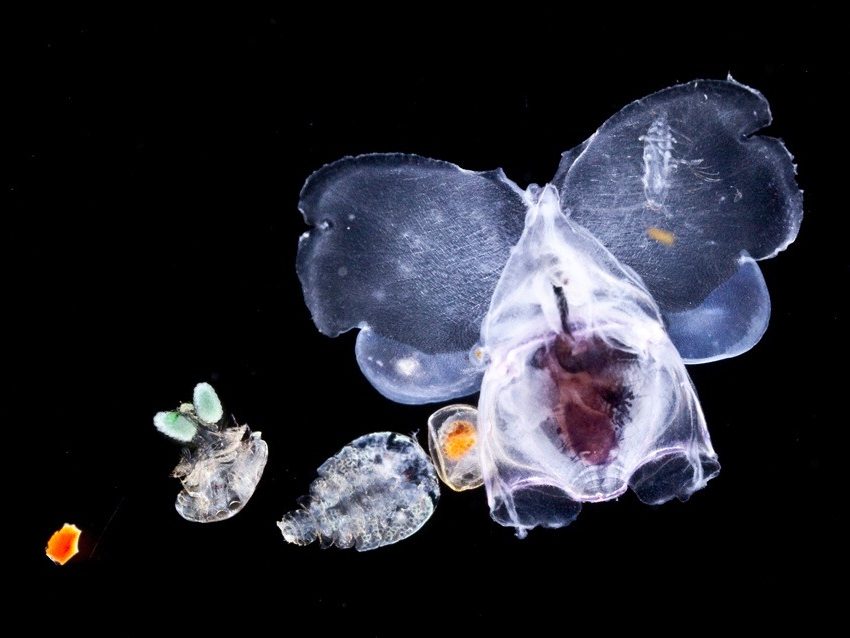
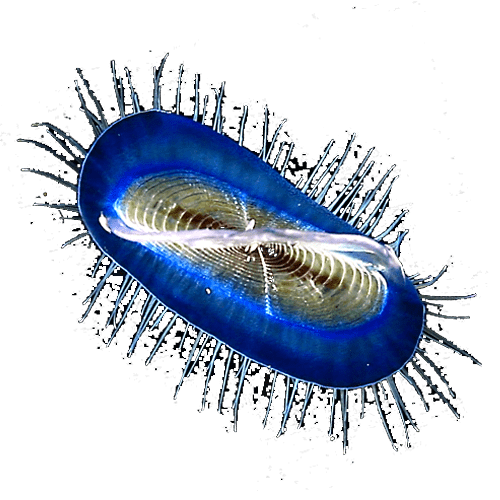
 Sea urchin larvaeParacentrotus lividus
Sea urchin larvaeParacentrotus lividus
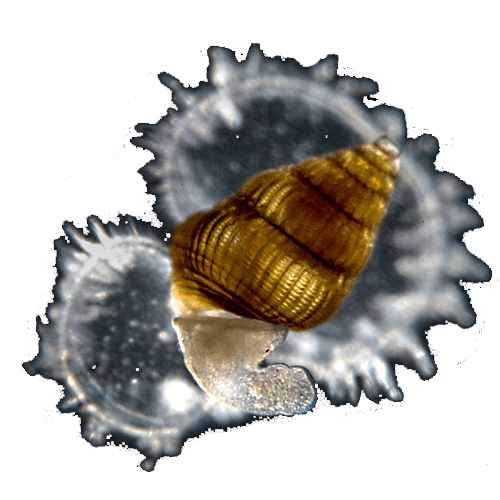
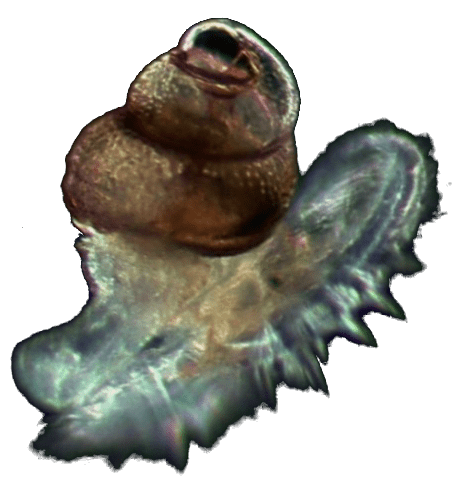 Veliger larva
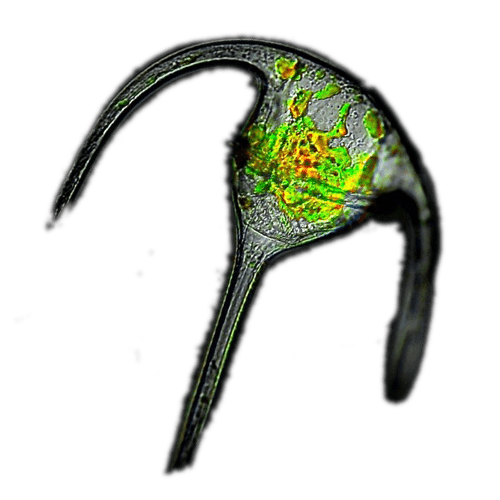
Veliger larva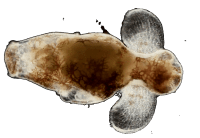 GymnosomePneumodermopsis paucidens
GymnosomePneumodermopsis paucidens
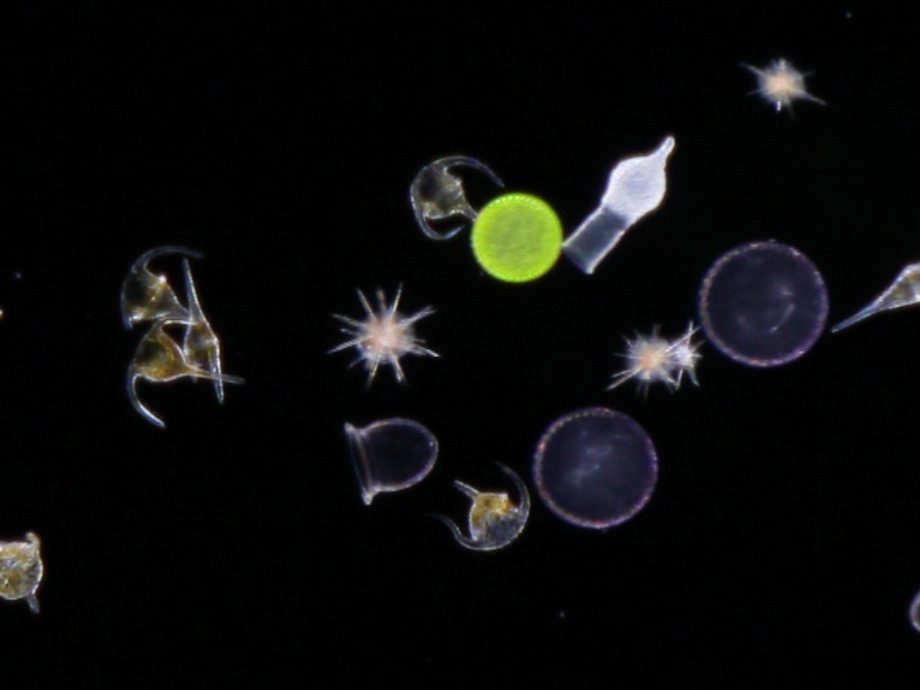
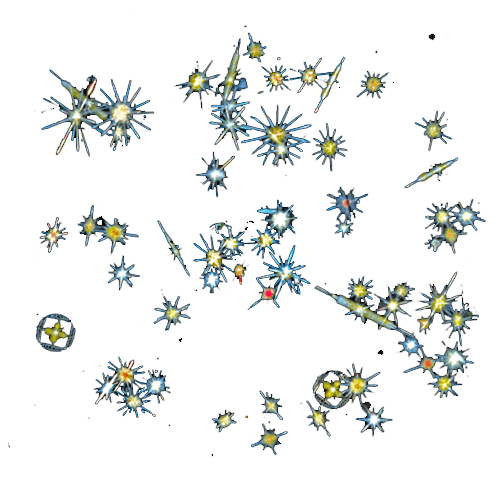
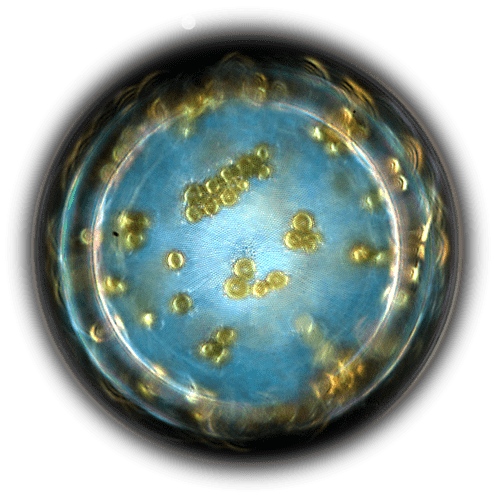
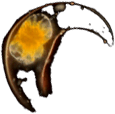 DinoflagellatePyrocystis elegans
DinoflagellatePyrocystis elegans Centric diatom
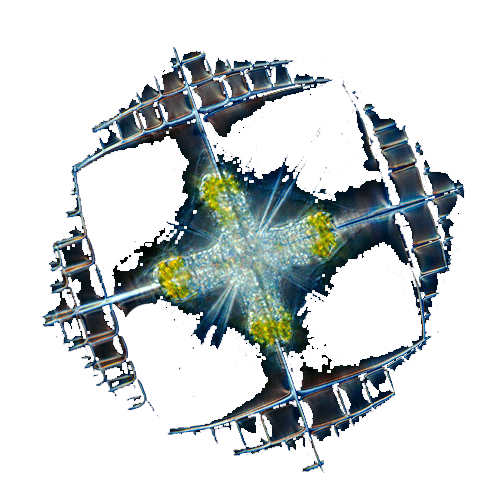
Centric diatom AcantharianLithoptera mulleri
AcantharianLithoptera mulleri RadiolarianAulacantha scolymantha
RadiolarianAulacantha scolymantha RadiolarianCollozum inerme
RadiolarianCollozum inerme
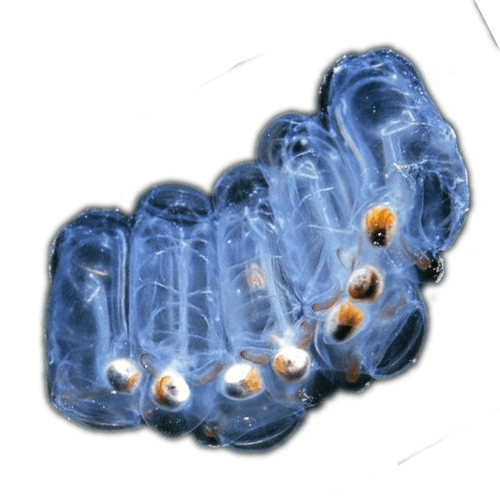
 Larvaceans
Larvaceans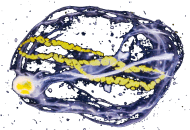 Salp
Salp
Photos
Narration
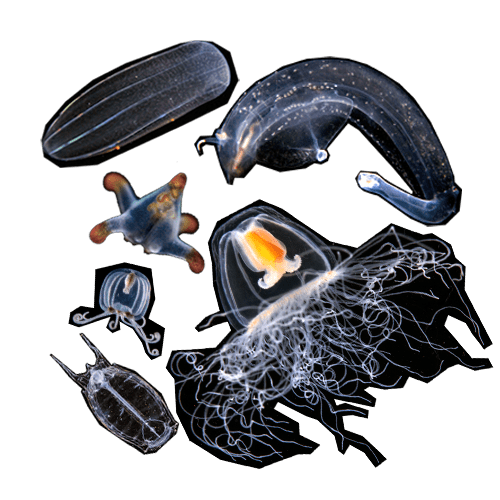
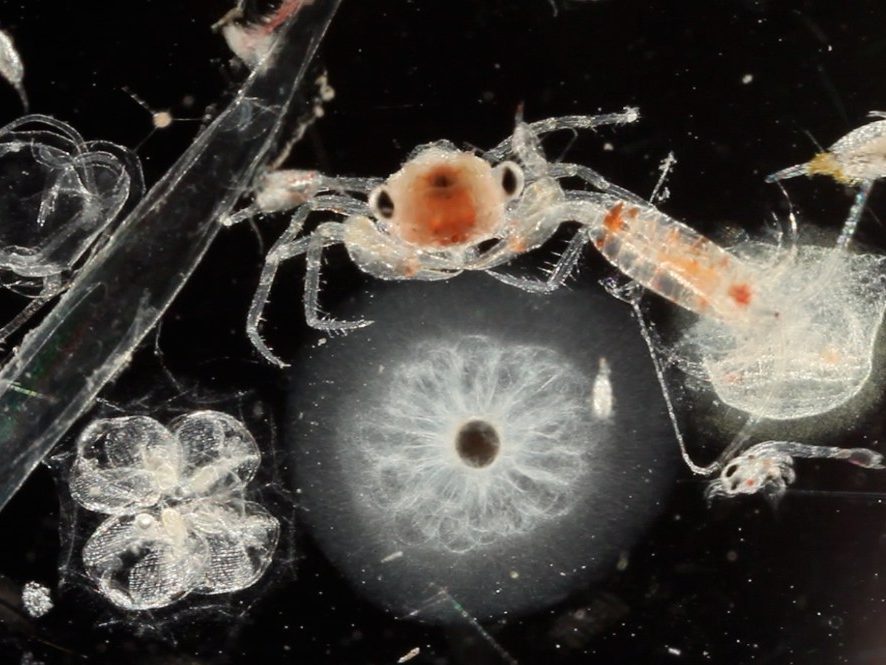
Plankton comes from the Greek word planktos, which means wandering or drifting. Any living creature carried along by ocean currents is classified as plankton. It ranges in size from the tiniest virus to siphonophores, the longest animals in the world, and also includes microscopic algae, krill or fish larvae.
Some plankton, like these jellyfish, salps, or sea gooseberries, drift all their lives. Others like pteropod molluscs and fish are only planktonic during their embryonic or larval life. When they reach adulthood, they settle or swim freely.
Planktonic organisms play important roles in human life. Many microscopic species get their energy from photosynthesis. They absorb carbon dioxide and produce oxygen. Thus, they constantly renew the air we breathe.
Plankton has also been a great provider of fossil energy. When planktonic organisms die, they sink to the sea-bed creating a layer of sediment. Over millions of years, this sediment fossilized, producing our precious oil.
Finally, plankton nourishes us: it is the basis of the food chain in which the large eat the small. Without plankton, there would be no fish!
Share this on
Production
CNRS Images
Original Idea
Christian Sardet
Director
Noé Sardet, Sharif Mirshak
Scientific consultant
Claude Carré
Texts
Sasha Bollet, Christian Sardet
Images
Sasha Bollet, Christian Sardet, Noé Sardet, Sharif Mirshak
Editing
Noé Sardet, Sharif Mirshak
Voice
Nick Storey
Sound Engineer
Noé Sardet, Sharif Mirshak
Director of production
Véronique Kleiner
Production assistant
Céline Ferlita
Translation
Theodore Rosengarten
Creative Commons Licence :
Attribution Non-Commercial
No Derivative